Do you eat fish?
 Protein and brain power are two words that should lure you in when you think of eating fish. Fish is a great source of lean protein, which is important for building and maintaining muscle and other tissues in your body. Fish is also a good source of iron, zinc, calcium, vitamin A and omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3’s help boost memory and support heart health. Docosahexaenoic acid, or DHA, is a type of omega-3 that is important for brain health, particularly with improved memory.
Protein and brain power are two words that should lure you in when you think of eating fish. Fish is a great source of lean protein, which is important for building and maintaining muscle and other tissues in your body. Fish is also a good source of iron, zinc, calcium, vitamin A and omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3’s help boost memory and support heart health. Docosahexaenoic acid, or DHA, is a type of omega-3 that is important for brain health, particularly with improved memory.
What about mercury?
Mercury is an environmental contaminant. When consumed in large amounts, mercury can be toxic to nerve cells, cause vision problems, and learning impairments. However, experts agree that fish has many benefits! The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have made recommendations on fish type and serving size to minimize the risk for mercury exposure.
So, how much is enough to reel in the benefits?
The 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends eating about 8 ounces per week of seafood for the general population.
The FDA and EPA recommend women of childbearing age (about 16-49 years old), especially pregnant and breastfeeding women, and children over the age of 10 eat 2-3 servings of fish a week from the “Best Choices” list or 1 serving from the “Good Choices” list below.
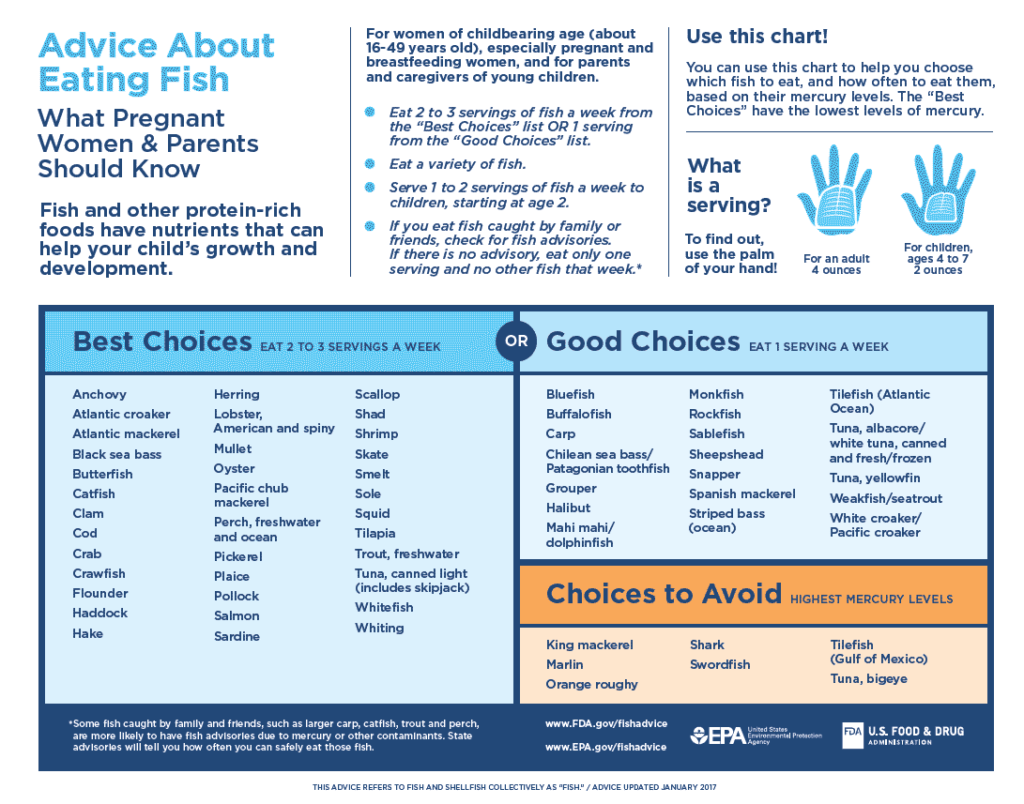 Children, starting at age 2, should be offered 1-2 servings of fish a week. Choose fish from the “Best Choices” list above, which contain the lowest levels of mercury.
Children, starting at age 2, should be offered 1-2 servings of fish a week. Choose fish from the “Best Choices” list above, which contain the lowest levels of mercury.
Not sure what a serving looks like? Use the palm of your hand to estimate an appropriate serving size (4 ounces) for adults. The palm of a child’s hand (4-7 years old) can be used to estimate an appropriate serving size (2 ounces) for children ages 2 and up.
When can your child start having fish?
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) has new recommendations for introducing highly-allergenic foods, including eggs, dairy, soy, peanuts, or fish. There is no evidence to support that waiting to introduce soft, allergy-causing foods beyond 6 months of age will prevent a food allergy. Unless there is family history of an allergen, you can begin to introduce these foods when your baby is ready for complementary foods at around 6 months of age!